Scripts
The extension is ps1
In PowerShell, the extension is ps1.
Create a script
To try it out, write the following in script.ps1.
"Hello World"
Run the script
To run the script, specify .\script-file-name.
PS> .\script.ps1
Hello World
Script file to accept input
To receive input in a script file, use Param().
Example script
To try it out, rewrite script.ps1 as follows.
param($name)
"Hello $name"
Execution Example
If you run the above script, you will see the following.
PS> .\script.ps1
Hello
PS> .\script.ps1 Bob
Hello Bob
Default input values
The default value of the input is specified by assigning it to a variable in Param.
Example Script
param($name="World")
"Hello $name"
Execution Example
PS> .\script.ps1
Hello World
PS> .\script.ps1 Bob
Hello Bob
Scripts that accept multiple inputs
You can also accept multiple inputs.
Example Script
param($name1="World1", $name2="World2")
"Hello $name1 $name2"
Execution Example
PS> ./script.ps1 Bob1 Bob2
Hello Bob1 Bob2
# It is better to specify the name of the parameter so that it is easier to understand what parameter is being specified.
PS> ./script.ps1 -name1 Bob1 -name2 Bob2
Hello Bob1 Bob2
Comment-based help
Comment-based help is a good way to explain a script or function.
So, you can easily understand the script when you look it up later.
Example scripts
In Visual Studio Code, you can type comm to get In Visual Studio Code,
you can easily enter a snippet of comment-based help by typing comm.
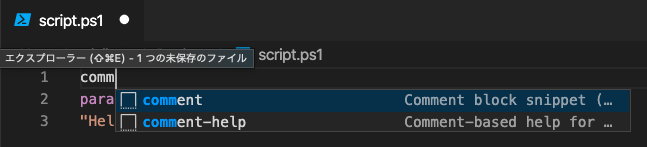
In the following example, I have rewritten the .EXAMPLE field.
<#
.SYNOPSIS
Short description
.DESCRIPTION
Long description
.EXAMPLE
PS C:\> ./script.ps1 Bob
Hello Bob
.INPUTS
Inputs (if any)
.OUTPUTS
Output (if any)
.NOTES
General notes
#>
param($name)
"Hello $name"
Execution Example
The Get-Help cmdlet can be used to view help for the target script.
PS> Get-Help ./script.ps1 -Detailed
NAME
/Users/miajimyu/Desktop/script.ps1
SYNOPSIS
Short description
# Omission
-------------------------- EXAMPLE 1 --------------------------
PS C:\>./script.ps1 Bob
Hello Bob